About CIC
Corporate Profile
Corporate Governance
Leadership
Organisation Structure
Procurement
Join Our Team
Media Centre
News and Updates
Publications
Contact Us
Registration Services
Construction Workers Registration
Construction Workers Registration System (CWRS)
Register of Construction Workers
Registered Specialist Trade Contractors Scheme
Technically Competent Persons Registration Scheme
Workers Information
Construction Workers Festival
Forms
Frequently Asked Questions
About the Scheme
Continuous Competence Development
Application for Registration
Technically Competent Persons List
About Construction Workers Registration Ordinance
About Application for Construction Workers Registration
About Submission of Daily Attendance Records
About “Designated Workers for Designated Skills” Provision
About Registered Specialist Trade Contractors Scheme
About Technically Competent Persons Registration Scheme
Trade Tests
Introduction
Civil & Building Construction Trades
Construction-related E&M Trades
Trade Test for Grade A Electrical Work
Machineries and Crane Operation
Other Skills Assessment
Trade Test Application for Repair, Maintenance, Alteration and Addition (RMAA) Works
Download Area
Frequently Asked Questions
Collaboration Scheme
Industry Development
Construction Business Development and Construction Productivity
Construction Digitalisation
Construction Innovation & Technology Application Centre (CITAC)
The Construction Innovation and Technology Fund (CITF)
Construction Safety
Environment & Sustainability
Mainland Affairs
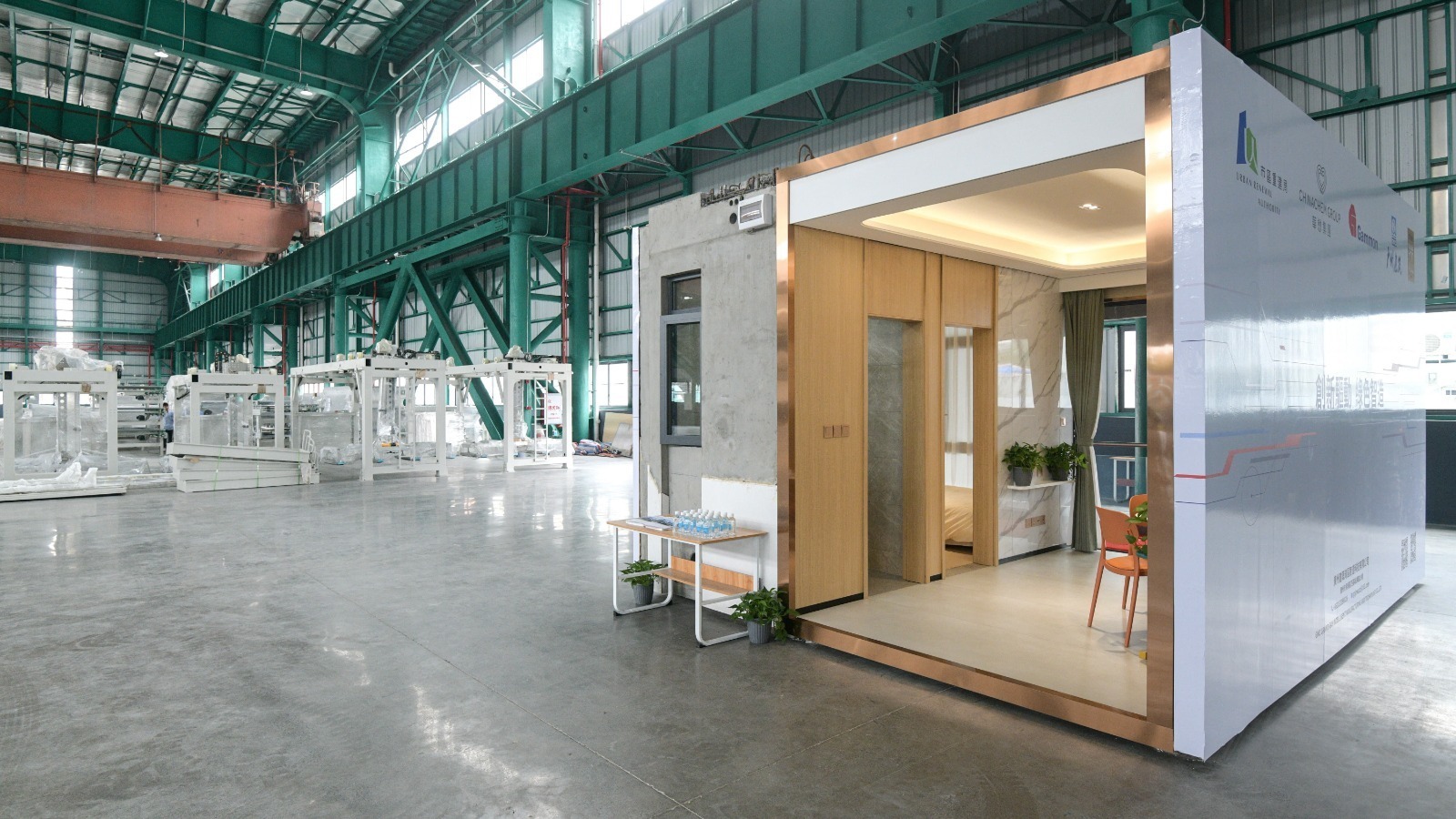
Modular Integrated Construction (MiC)
Repair, Maintenance, Alteration and Addition
CIC-Zero Carbon Park
iHub
Industry Development Webinars